
- +91-8808808186
- 11:00 AM - 01:00 PM | 04:00 PM - 06:00 PM
Best Robotic, Laparoscopic, Bariatric, Gastrosurgeon of Surat

Dr Dharmesh Dhanani
MS, FNB (Minimal Access Surgery), FACS, FALS, FMAS, FAIS
Consultant Gastrosurgeon, Bariatric & Laparoscopic Surgeon
Liver cancer is a serious condition characterized by the uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells in the liver, one of the most vital organs in the body. It is a leading cause of cancer-related deaths globally, making early detection and intervention critical.
What Causes Liver Cancer?
Liver cancer typically occurs in individuals who have chronic liver diseases, such as cirrhosis or hepatitis. Cirrhosis, which is the scarring of liver tissue, often results from long-term liver damage. Some common causes of cirrhosis include:
- Chronic viral infections like hepatitis B or C
- Excessive alcohol consumption
- Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)
When the liver is repeatedly damaged, its attempts to repair itself can increase the risk of developing cancerous cells.
Other contributing risk factors for liver cancer include:
- Age and Gender: People over 50, particularly men, are at a higher risk of developing liver cancer.
- Genetics: Certain inherited conditions like hemochromatosis and Wilson’s disease can elevate the risk.
- Obesity: Excess weight and associated conditions such as diabetes increase the likelihood of liver cancer.
- Exposure to Aflatoxins: Aflatoxins, which are toxins produced by certain molds that contaminate food, can contribute to liver cancer development.
What Are the Symptoms of Liver Cancer?
Liver cancer often doesn’t present symptoms until it has progressed. Early signs can be subtle, but as the disease advances, the following symptoms may occur:
- Unexplained Weight Loss: Significant, unintentional weight loss may indicate liver cancer, especially when accompanied by other symptoms.
- Abdominal Pain and Swelling: Pain in the upper abdomen, along with swelling caused by fluid buildup, is common in liver cancer.
- Jaundice: Yellowing of the skin and eyes, known as jaundice, can occur when the liver is unable to properly process bilirubin, a substance produced when red blood cells are broken down.
- Loss of Appetite and Fatigue: A noticeable decline in appetite and persistent fatigue are typical in individuals with liver cancer.
- Nausea and Vomiting: As the cancer grows, nausea and vomiting may occur due to the liver’s inability to function properly.
These symptoms can also be caused by other liver conditions, which is why seeking medical attention early is crucial for accurate diagnosis.
How is Liver Cancer Diagnosed and Staged?
Diagnosing liver cancer involves several tests, which help confirm the presence of cancer and determine its stage. These may include:
- Blood tests to check for liver function and cancer markers.
- Imaging studies like CT scans or MRIs to detect tumors.
- Liver biopsy to obtain a tissue sample for examination.
Liver cancer is staged based on how far it has spread. The stages range from localized tumors to advanced cancer that has spread to other parts of the body.
Treatment Options for Liver Cancer
The appropriate treatment for liver cancer depends on factors such as the cancer’s stage, the patient’s overall health, and the function of the liver. Treatment options include:
- Surgery: In some cases, the tumor may be surgically removed (resection), or a liver transplant may be necessary if the cancer has severely damaged the liver.
- Ablation Therapy: This technique destroys cancer cells using heat (radiofrequency ablation) or microwave energy.
- Radiation Therapy: High-energy radiation is directed at cancer cells to shrink tumors and prevent growth.
- Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy may be used to treat cancer cells, either systemically or in specific regions of the liver.
- Targeted Therapy: Targeted drugs focus on specific molecules involved in the growth of cancer cells, inhibiting tumor development.
- Immunotherapy: This treatment boosts the body’s immune system to help it fight off cancer cells more effectively.
Treatment may involve a combination of these therapies, depending on the patient’s condition.
Prevention and Prognosis
While liver cancer cannot always be prevented, adopting certain lifestyle changes can lower the risk of developing this disease:
- Limit alcohol consumption: Excessive drinking can damage the liver over time.
- Vaccination: Vaccination against hepatitis B can help prevent liver cancer linked to chronic hepatitis infections.
- Maintain a healthy weight: A balanced diet and regular exercise can reduce the risk of obesity-related liver issues.
- Regular check-ups: If you have chronic liver conditions, regular screening can help detect liver problems early.
The prognosis for liver cancer depends on several factors, such as the stage at diagnosis and the patient’s overall health. Early diagnosis and treatment greatly improve the chances of survival and successful outcomes.
Conclusion
Liver cancer is a challenging disease, but understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatment options can make a significant difference in your health journey. With advancements in medical research and treatment techniques, patients have a better chance at recovery, especially when diagnosed early.
If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms or is at increased risk of liver cancer, it’s crucial to consult with a specialist. Dr.Dharmesh Dhanani, one of Surat’s leading gastro cancer surgeons with over 15 years of experience, offers expert consultation and treatment for liver cancer. His commitment to personalized care ensures the best possible outcomes for his patients.
Don’t wait for symptoms to worsen—seek medical attention early for better treatment results.
On Dr Dharmesh Dhanani
Related Posts

Understanding Minimally Invasive Surgery for GI Cancers – What Patients in Surat Need to Know
When it comes to treating gastrointestinal (GI) cancers, early diagnosis and advanced surgical techniques can make a life-saving difference. At Kiran Hospital, Surat, Dr. Dharmesh Dhanani, a renowned GI cancer and laparoscopic gastrosurgeon, is transforming cancer care through minimally invasive surgeries.we’ll help you understand what minimally invasive GI cancer surgery
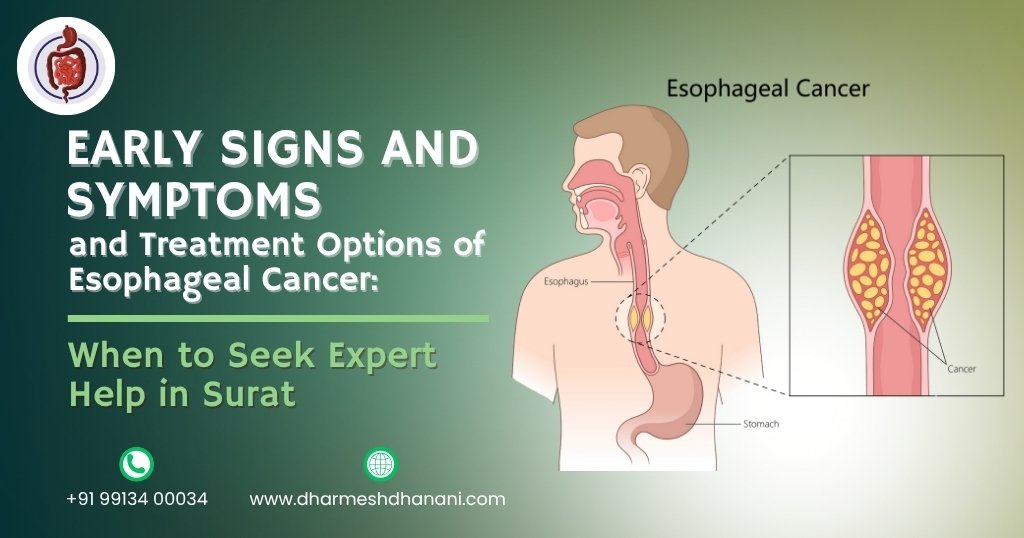
Early Signs and Symptoms and Treatment Options of Esophageal Cancer: When to Seek Expert Help in Surat
Esophageal cancer, a serious condition affecting the food pipe (esophagus), is often diagnosed late due to subtle early symptoms. Early detection is crucial to improve survival and treatment success. In Surat, patients can access world-class care with Dr. Dharmesh Dhanani, a highly experienced Gastrointestinal Cancer Surgeon and Senior Consultant at

Liver Abscess: Causes, Symptoms & Best Treatment Options | Dr. Dharmesh Dhanani – Best HPB Surgeon in Surat
What is a Liver Abscess? A liver abscess is a pus-filled cavity within the liver caused by an infection. It results from bacteria, parasites, or fungi invading the liver tissue and forming a localized collection of pus. If not detected and treated early, a liver abscess can rupture and spread

Understanding Gallbladder Cancer: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options in Surat
Gallbladder cancer is a rare but potentially dangerous form of cancer that starts in the gallbladder, a small organ located just beneath the liver. While it is not as commonly diagnosed as other types of cancer, it can be life-threatening, particularly when detected in later stages. In this blog, we